(BMJ)—A man in his 30s presented with a 3-month hx of an unusual odor from the armpits. On exam, axillary hair shafts were encircled by what appeared to be soft yellow-white material. Hair roots and adjacent skin weren't affected. Dermoscopy with polarized light showed yellowish-white creamy concretions adherent to several hair shafts. Under UV light, concretions exhibited green, purple, and red fluorescence. What's the dx?

|
poliosis
|
|
trichomycosis axillaris
|
|
white piedra
|
|
seborrheic dermatitis
|
Can you identify this pill?
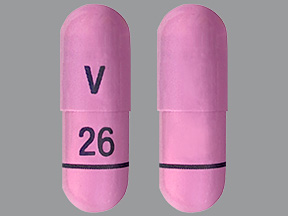
|
droxidopa
|
|
hydroxyurea
|
|
fluvastatin
|
|
amoxicillin
|
(PubMed)—A 73-yo woman with hypertension, atrial fibrillation, hyperlipidemia, diabetes mellitus, and metastatic HR-positive, HER-2 negative breast cancer presented with general weakness and muscle pain in the lower extremities as well as brown-colored urine. Admission labs: Cr 2.06 mg/dL, GFR 14 mL/min, CPK 3070 U/L; U/A: moderate myoglobinuria.
The patient was diagnosed with acute kidney injury secondary to rhabdomyolysis.
Meds: apixaban, bisoprolol, insulin glargine, ribociclib, simvastatin, valsartan-hydrochlorothiazide.
What drug combo could have caused the rhabdomyolysis?
The patient was diagnosed with acute kidney injury secondary to rhabdomyolysis.
Meds: apixaban, bisoprolol, insulin glargine, ribociclib, simvastatin, valsartan-hydrochlorothiazide.
What drug combo could have caused the rhabdomyolysis?

|
apixaban and valsartan
|
|
hydrochlorothiazide and simvastatin
|
|
ribociclib and simvastatin
|
Which of these strategies has NOT been proven to help with thinning/lackluster hair, brittle nails, or keeping skin smooth and healthy?

|
Taking collagen drinks and supplements to support skin, hair, and nail tissues
|
|
Quitting smoking
|
|
Limiting alcohol to two drinks or less a day for men and one drink or less in a day for women
|
|
Applying sunscreen daily and remembering to reapply every two hours
|
|
Following a healthy lifestyle, including eating a balanced diet that includes protein-rich foods
|
|
Wearing wide-brimmed or UV-protective hats and clothing when spending a lot of time in the sun
|
Which of these strategies has NOT been proven to help with thinning/lackluster hair, brittle nails, or keeping skin smooth and healthy?

|
Taking collagen drinks and supplements to support this major structural protein in our tissues.
|
|
For smokers: Quitting smoking.
|
|
Applying sunscreen daily and remembering to reapply every 2 hours.
|
|
Limiting alcohol to 2 drinks or less in a day for men or 1 drink or less in a day for women.
|
|
Wearing wide-brimmed or UV-protective hats and clothing when spending a lot of time in the sun.
|
|
Following a healthy lifestyle and eating a balanced diet that includes protein rich foods.
|
