Which of these is the most common in-flight medical emergency?

|
cardiac symptoms (chest pain, palpitations, pacemaker concerns)
|
|
nausea/vomiting
|
|
syncope or presyncope
|
|
seizures
|
|
obstetric or gynecological problems
|
|
respiratory symptoms
|
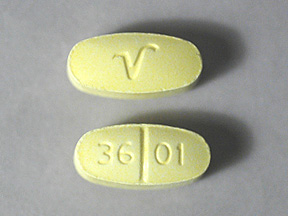
Can you identify this pill?
|
levetiracetam
|
|
paricalcitol
|
|
abacavir
|
|
hydrocodone/acetaminophen
|
All of these are early stage or late stage symptoms of primary amebic meningoencephalitis (PAM) except for:
|
cercarial dermatitis
|
|
stiff neck
|
|
coma
|
|
severe frontal headache
|
|
fever
|
|
seizures
|
|
altered mental status/hallucinations
|
|
nausea/vomiting
|
(Eur Heart J Case Rep)—A 57-year-old male with history of heart transplant (6 years prior), acute lymphocytic leukemia (diagnosed 14 years prior and treated via allogeneic stem cell transplant), CKD, hypothyroidism, HTN, anemia, and gout presented with severe fatigue and shortness of breath. Physical examination was notable for pallor and trace lower-extremity edema. Lab data revealed pancytopenia, with WBC 0.6 x 103/μL (normal 4.5-11.0 x 103/μL), Hgb 6.3 g/dL (13.9-16.3 g/dL), and platelets 41 x 103/μL (150-450 x 103/μL). Given the lack of evidence of malignancy on peripheral blood smear and bone marrow bx, as well as negative viral studies, drug-induced myelosuppression was considered in the differential.
Meds: azathioprine, tacrolimus, allopurinol, diltiazem, epoetin alfa, folic acid, hydralazine, levothyroxine, and torsemide.
Which drug combo could have caused the pancytopenia?
Meds: azathioprine, tacrolimus, allopurinol, diltiazem, epoetin alfa, folic acid, hydralazine, levothyroxine, and torsemide.
Which drug combo could have caused the pancytopenia?

|
azathioprine and allopurinol
|
|
epoetin alfa and tacrolimus
|
|
tacrolimus and torsemide
|
|
allopurinol and hydralazine
|
