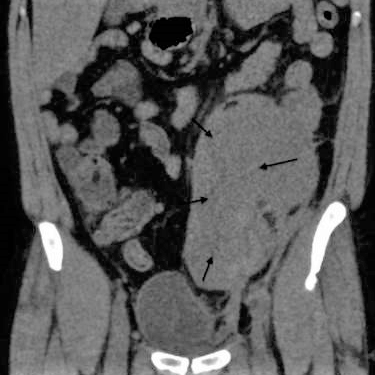
(Cureus)—A 40-year-old woman with hx of HIV, coronary artery disease, peripheral vascular disease, and polysubstance abuse presented with critical limb ischemia of the right leg. The patient received a femoral artery stent, and apixaban 2.5 mg bid was started. The patient returned with low back pain 1 week postdischarge, and a CT scan demonstrated a large retroperitoneal hematoma.
Meds: clopidogrel, darunavir/cobicistat, abacavir/dolutegravir/lamivudine, atorvastatin, isosorbide dinitrate, and hydralazine.
Which drug combo could have caused the hematoma?
Meds: clopidogrel, darunavir/cobicistat, abacavir/dolutegravir/lamivudine, atorvastatin, isosorbide dinitrate, and hydralazine.
Which drug combo could have caused the hematoma?
|
clopidogrel and atorvastatin
|
|
clopidogrel and darunavir/cobicistat
|
|
apixaban and abacavir/dolutegravir/lamivudine
|
|
apixaban and darunavir/cobicistat
|
(Cancer Rep)—A 62-year-old woman with DM, dyslipidemia, HTN, renal impairment, and HR-positive, HER-2 negative metastatic breast cancer presented with a 1-wk hx of progressive dyspnea, intermittent epigastric pain, and nausea approximately 2mo after starting ribociclib. Admission labs: BUN 56 mg/dL, Cr 2.8 mg/dL, sodium 133 mEq/L, potassium 5.6 mEq/L, chloride 102 mEq/L, bicarbonate 6 mEq/L, CPK 715 U/L, glucose 217 mg/dL, lactate 13.7 mmol/L, pH 7.12, pCO2 20.8 mm Hg, Po2 66.8 mm Hg, anion gap 25.
The patient was diagnosed with severe lactic acidosis and acute respiratory failure.
Meds: metformin, glipizide, losartan, amlodipine, simvastatin, ribociclib, fulvestrant.
Which drug combo could have caused the lactic acidosis?
The patient was diagnosed with severe lactic acidosis and acute respiratory failure.
Meds: metformin, glipizide, losartan, amlodipine, simvastatin, ribociclib, fulvestrant.
Which drug combo could have caused the lactic acidosis?

|
ribociclib and metformin
|
|
metformin and simvastatin
|
|
fulvestrant and losartan
|
|
amlodipine and glipizide
|
(epocrates)—The absorption of the oral antifungal itraconazole is sensitive to changes in gastric pH. For example, gastric acid suppressors such as H2-receptor antagonists and proton pump inhibitors commonly result in a decrease in itraconazole absorption, and hence a potential decrease in efficacy.
Which formulation of itraconazole has been linked w/ increased systemic exposure when co-administered w/ acid suppressors?
Which formulation of itraconazole has been linked w/ increased systemic exposure when co-administered w/ acid suppressors?

|
itraconazole 100-mg capsule
|
|
itraconazole 10-mg/mL solution
|
|
itraconazole 200-mg tablet
|
|
itraconazole 65-mg capsule
|
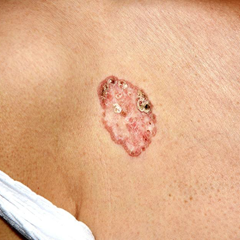
(BMJ)—A woman in her 80s had a persistent, mildly itchy lesion on her R chest x3y in an area frequently exposed to sun in the summer, when she’d usually wear vests. The lesion improved only slightly with topical steroids and antifungals. Exam: annular red plaque with crusts and scales. Potassium hydroxide test negative. What’s the dx?
|
Porokeratosis of Mibelli
|
|
Basal cell carcinoma
|
|
Chronic eczema
|
|
Bowen disease
|
|
Tinea corporis
|
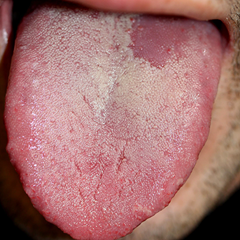
(BMJ)—A nonsmoking man in his 30s had asymptomatic tongue lesions found during a derm eval. PMHx: psoriasis, no alcohol misuse. Exam: thick, scaly red plaques on scalp, back, and limbs. Tongue: reddish area with absent papillae; branching fissures. What’s the dx?
|
Erythematous candidiasis
|
|
Leukoplakia
|
|
Erythroplakia
|
|
Lichen planus
|
|
Geographic tongue
|
