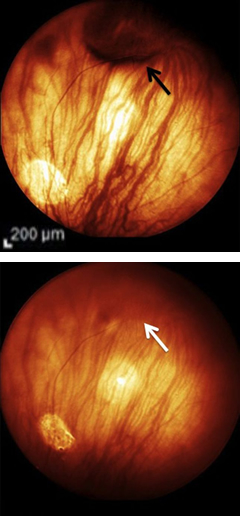
A 45-yo man was referred for a suspected choroidal melanoma (black arrow). The lesion increased in size on upgaze, but disappeared completely with gentle pressure applied to globe (white arrow). What is the diagnosis?
|
Choroidal melanoma
|
|
Toxoplasmosis retinochoroiditis
|
|
CNS tumor metastasis
|
|
Cotton wool spot
|
|
Vortex vein varix
|
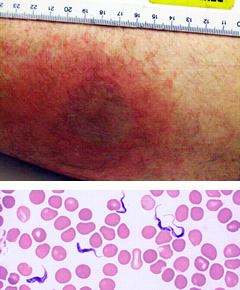
A 58-yo man who recently visited Zambia presents w/ fevers and lethargy. Painful leg swellings 3 days earlier. Malaria test negative. Exam: GCS 12/15, facial swelling, indurated skin lesions. Blood film: extracellular structures. What is the diagnosis?
|
Secondary syphilis
|
|
Human African trypanosomiasis
|
|
Dengue fever
|
|
Malaria
|
|
Leptospirosis
|
