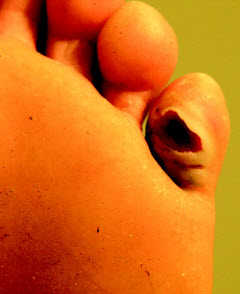
(BMJ) - A 14-yo girl presented w/ a swollen, ulcerated 5th toe. Sx began 8 days prior when she felt severe pain in her toe while wading in the English Channel, followed by swelling of her entire lower leg. What is the diagnosis?
|
Mycobacterium marinum infection
|
|
Stingray envenomation
|
|
Weever fish sting
|
|
Blue jellyfish sting
|
|
Sea urchin puncture wound
|
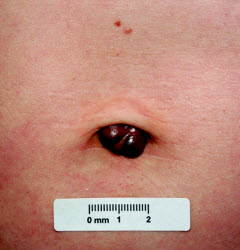
(BMJ) - A 34-yo woman presented w/ a tender, purple-brown nodule in her umbilicus. She had no unusual menstrual sx and had a recent uncomplicated pregnancy. Biopsy confirmed the diagnosis. What is it?
|
Sister Mary Joseph nodule
|
|
Pyogenic granuloma
|
|
Umbilical endometriosis
|
|
Umbilical hernia
|
|
Malignant melanoma
|
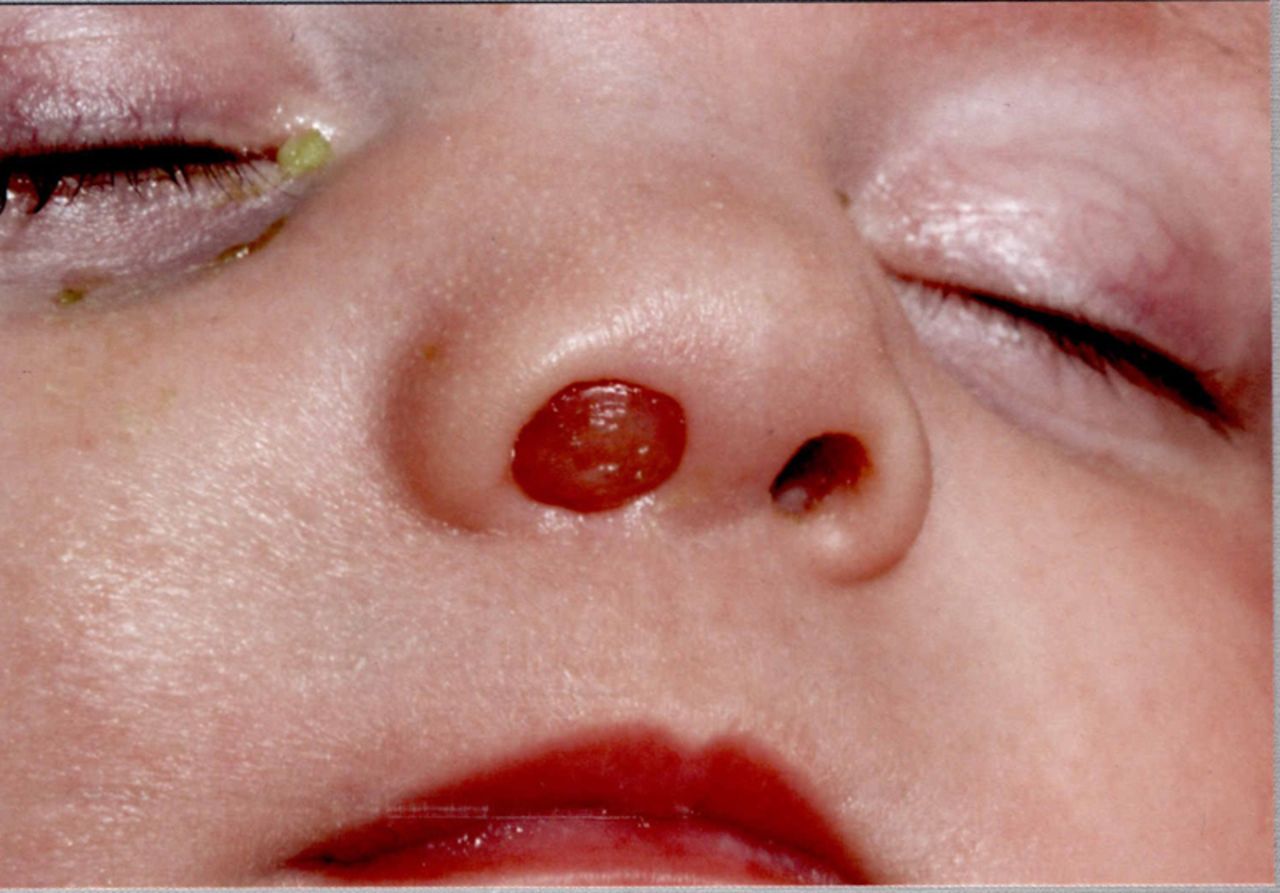
(BMJ) - A newborn presented w/ a fleshy lump in his nostril. CT scan confirmed the diagnosis, and it was successfully treated w/ a surgical procedure. What is it?
|
Nasal dermoid
|
|
Naso-ethmoidal meningocele
|
|
Choanal atresia
|
|
Foreign body
|
|
Dacryocystocele
|
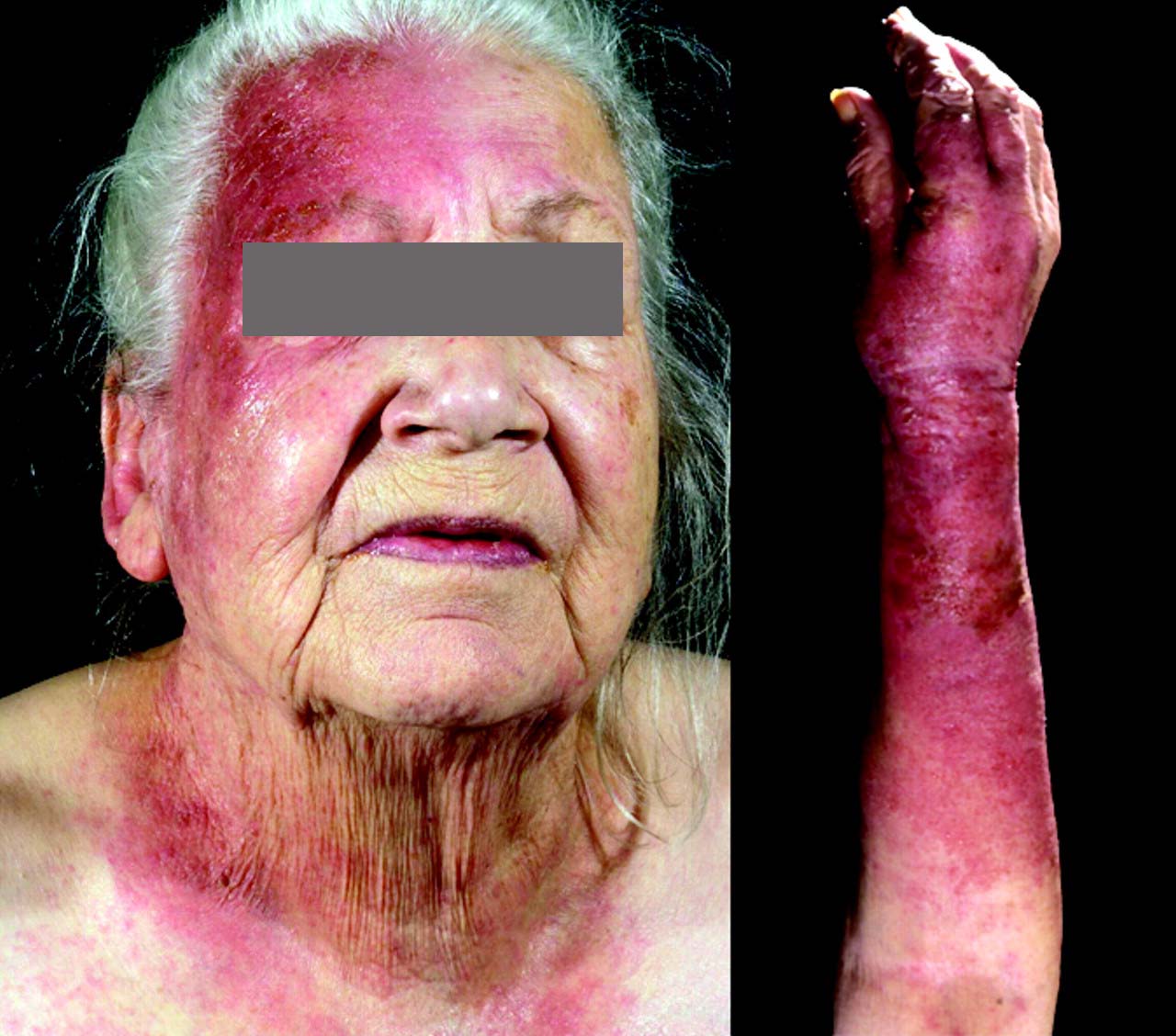
(BMJ) - A 76-yo woman had a 6-wk hx of presumed erysipelas, which did not respond to several courses of oral and IV abx. Exam: eczematous rash affecting the right cheek, right forehead, and right forearm; her left side was unaffected. Patient stated that she slept on her right side. What is the diagnosis?
|
Sweet syndrome
|
|
Lichen simplex chronicus
|
|
Herpes zoster
|
|
Harlequin syndrome
|
|
Allergic contact dermatitis
|
(BMJ) - A full-term neonate was born w/ a mass on his leg and asymptomatic ASD and VSD. Exam: large, violaceous mass with grey/purple halo on left thigh. US: highly vascularized mass confined to the SC tissue. By 9 mo, the mass had completely regressed. What is the diagnosis?
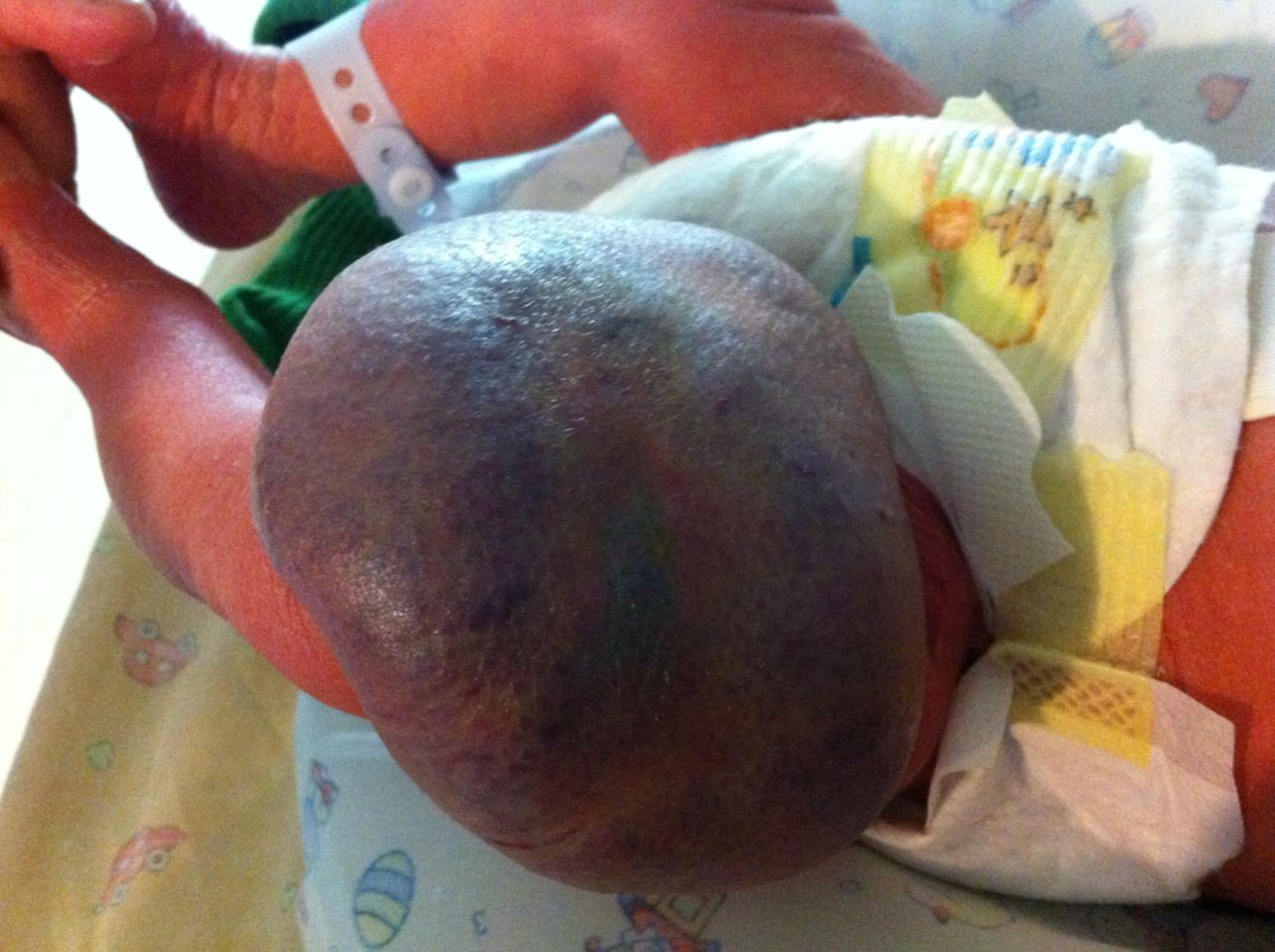
|
Rapidly involuting congenital hemangioma (RICH)
|
|
Cobb syndrome
|
|
Infantile hemangioma
|
|
Dabska tumor
|
|
Pyogenic granuloma
|
