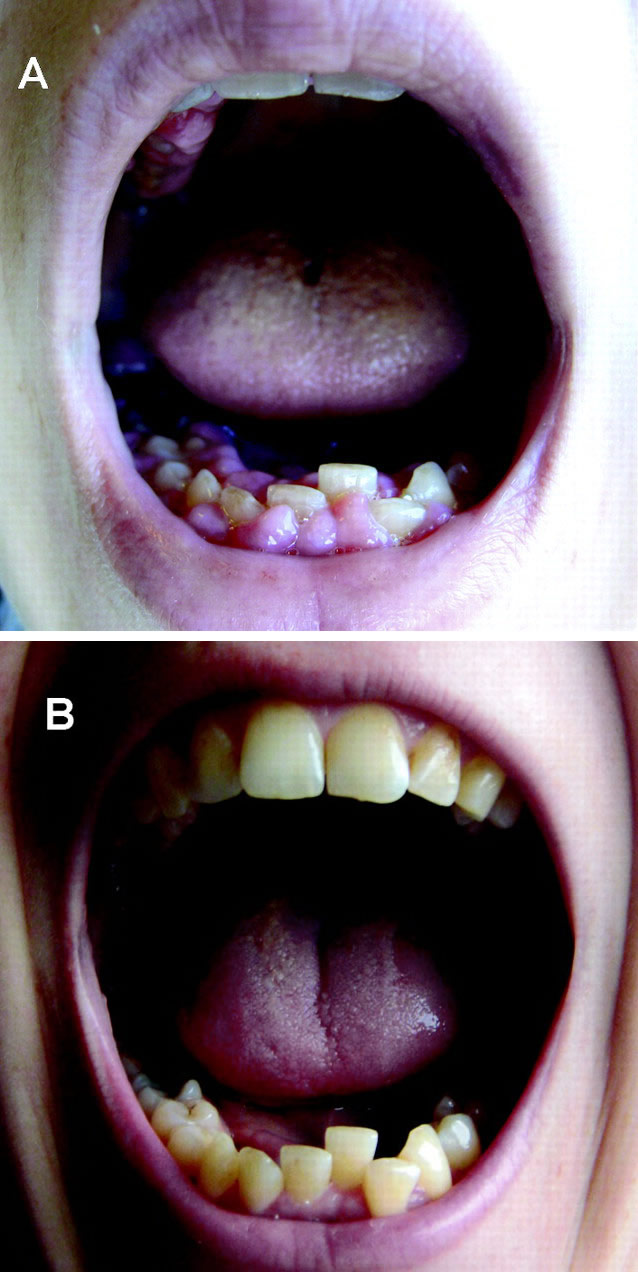
(BMJ) - A 35-yo pregnant woman developed gingival hyperplasia and lost 10 lbs over 5 wks w/ no other symptoms. Labs: leukocytosis, anemia, thrombocytopenia. Images show gums before and after resolution. What is the diagnosis?
|
Infectious gingivitis
|
|
HIV infection
|
|
Pregnancy-related gingival hypertrophy
|
|
Acute myeloblastic leukemia
|
|
Crohn disease
|
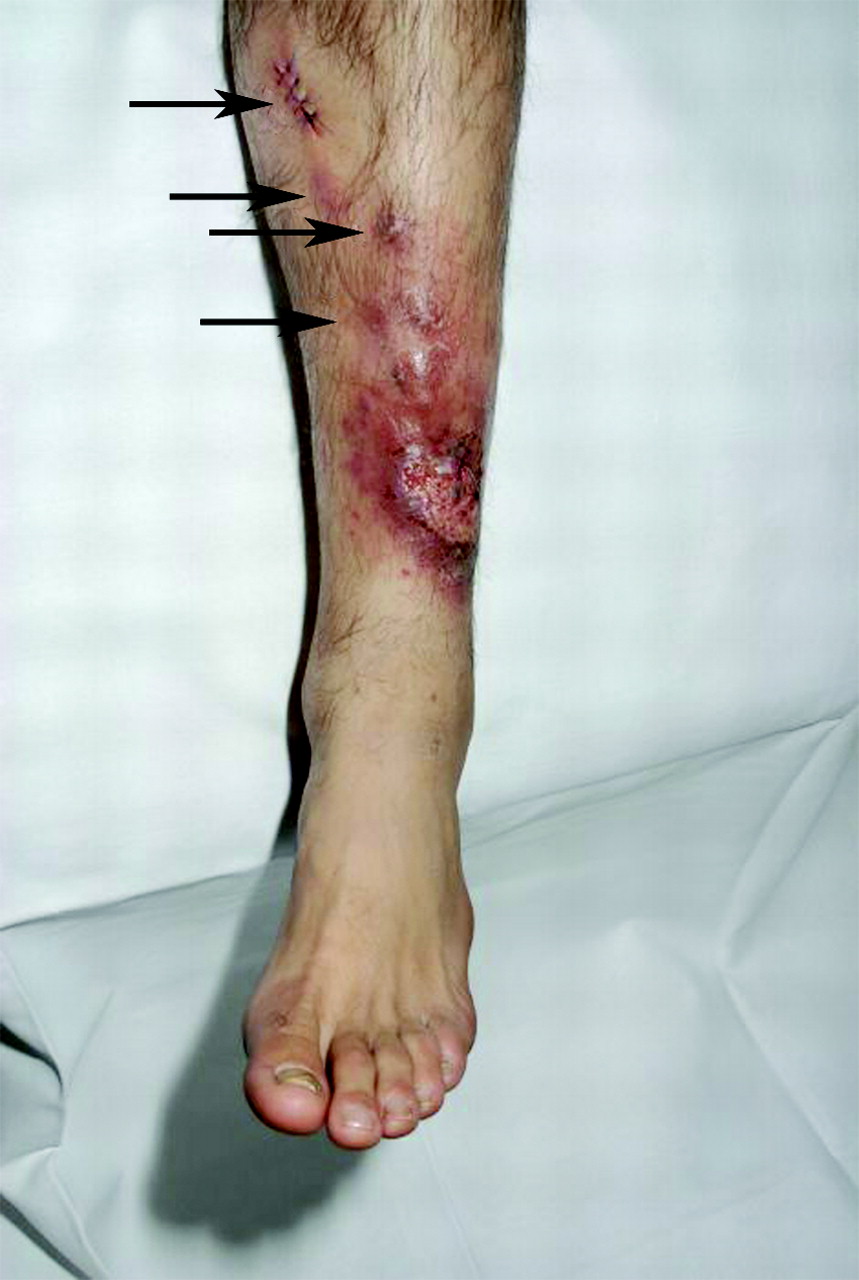
(BMJ) – A 40-yo man presented w/ a 6-wk hx of a mildly painful, enlarging ulcer on his lower leg after a trip to Afghanistan. Exam showed a large ulcer and proximal erythematous nodules. What is the diagnosis?
|
Ulceroglandular tularemia
|
|
Cutaneous leishmaniasis
|
|
Pyogenic granuloma
|
|
Sporotrichosis
|
|
Leprosy
|
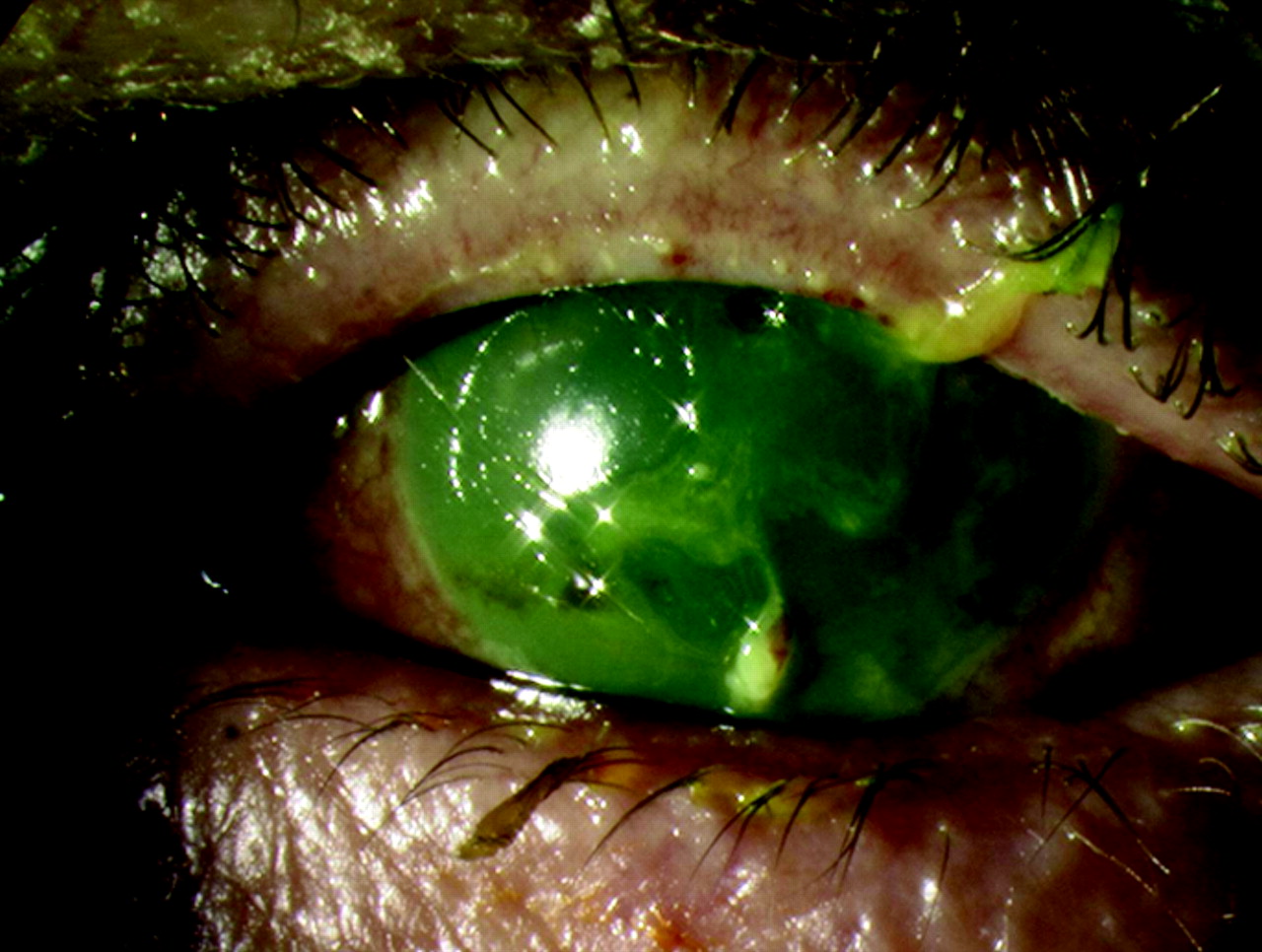
(BMJ) - A patient presented w/ eye complaints 36 hours after a car crash w/ airbag deployment. Fluorescein staining revealed diffuse uptake and corneal opacification. What is the diagnosis?
|
Corneal abrasion
|
|
Acute angle-closure glaucoma
|
|
Ruptured globe
|
|
Alkaline chemical burn
|
|
Bacterial keratitis
|
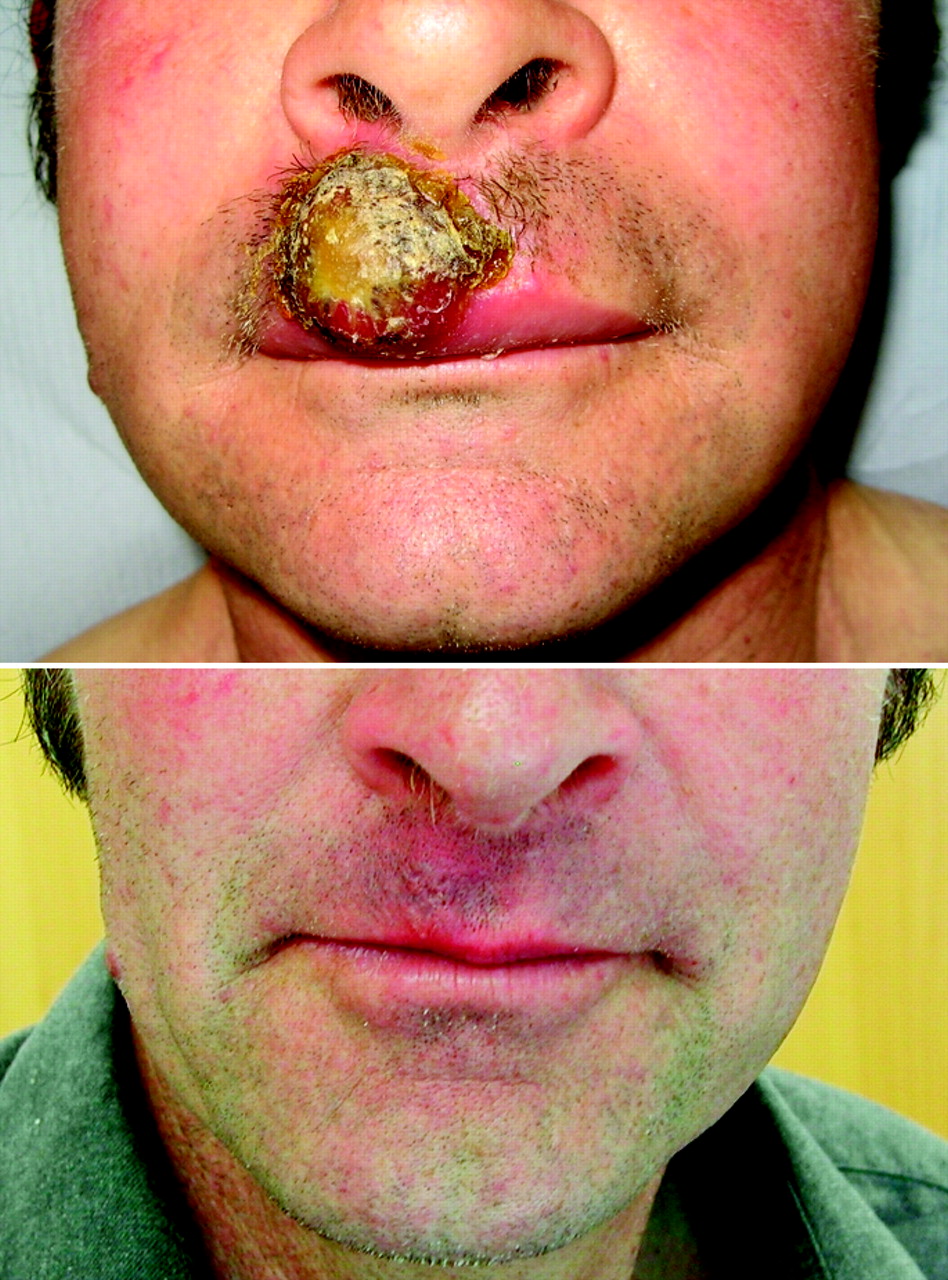
(BMJ) - A 56-yo sheep farmer presented w/ a lip lesion 3 wks after being butted on the mouth by a lamb. Biopsy showed no virus particles but confirmed the diagnosis. Images show lesion before and after tx w/ clobetasol propionate. What is it?
|
Impetigo
|
|
Tick bite
|
|
Orf virus infection
|
|
Pyogenic granuloma
|
|
Syphilis
|
(BMJ) - A 40-yo man presented w/ polyarthralgia, chest pain, and malaise w/ tenderness and elevation of the “tree trunk” of his 20-yo tattoo. Chest CT showed hilar lymphadenopathy and interstitial changes. Skin bx confirmed the diagnosis. What is it?
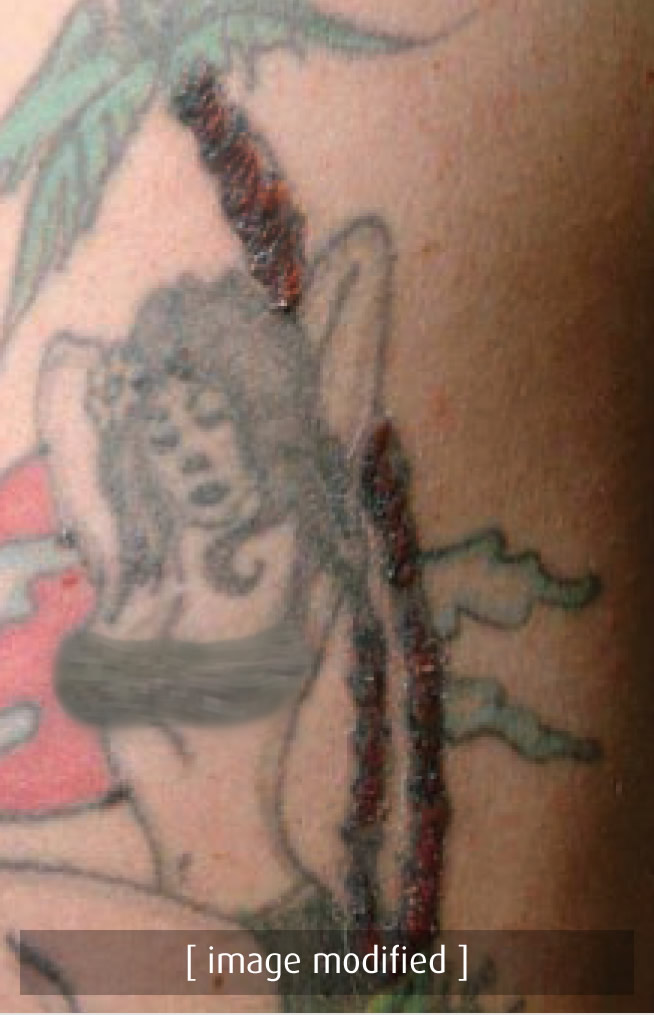
|
Lymphoma
|
|
Histoplasmosis
|
|
Tuberculosis
|
|
Sarcoidosis
|
|
Nontuberculous mycobacteria (NTM) infection
|
(BMJ) - A 31-yo Romanian painter and decorator had a bluish line on his gums and iron-deficiency anemia w/ basophilic stippling on blood smear. A blood test confirmed the cause. What is the diagnosis?
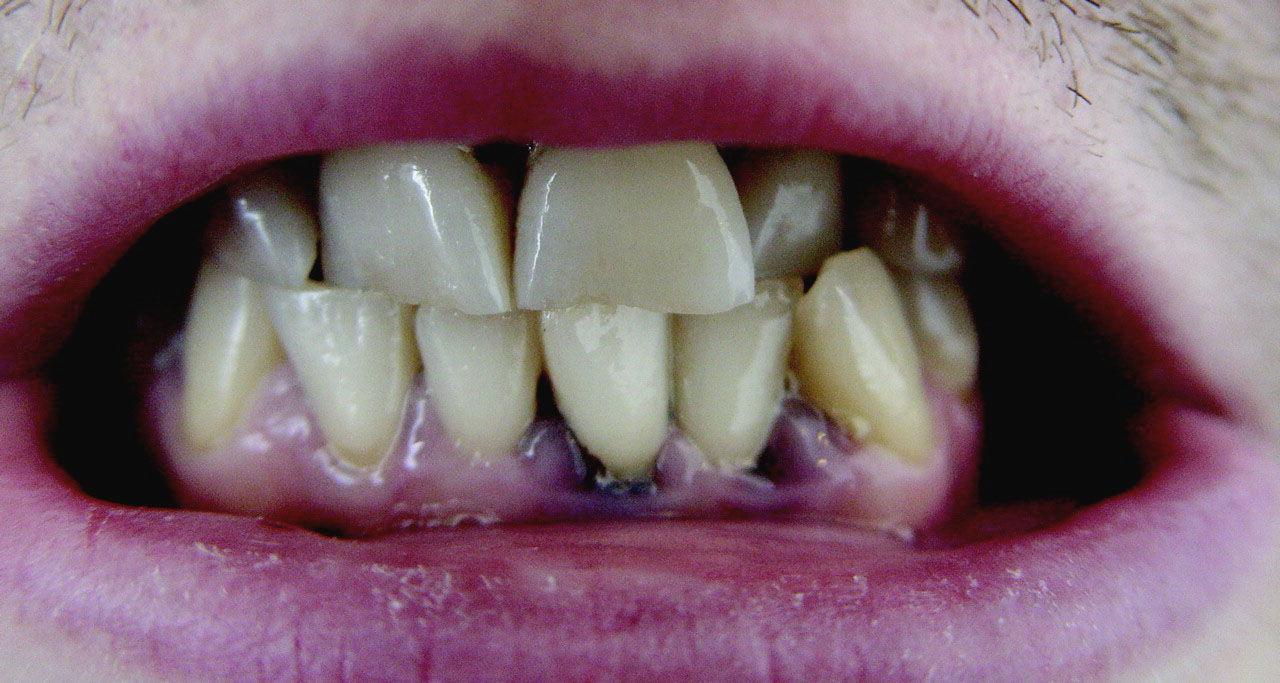
|
Gingivitis
|
|
Lead poisoning
|
|
Scurvy
|
|
Methamphetamine toxicity
|
|
Bismuth ingestion
|
(BMJ) - A 16-yo girl with history of atopic eczema developed multiple, painful, punched-out erosions over her forehead and eyelids after exposure to a person with cold sores. What is the diagnosis?
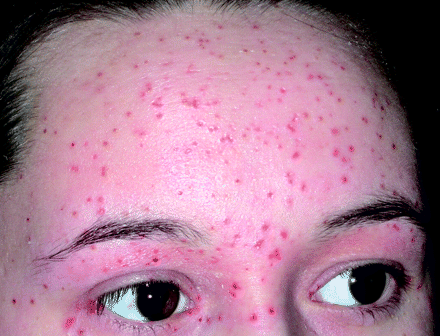
|
Eczema herpeticum
|
|
Contact dermatitis
|
|
Bullous impetigo
|
|
Disseminated gonorrhea
|
|
Coxsackie virus infection
|
(BMJ) - A 38-yo sheep farmer had an itchy, painful, blistering eruption on his ear that occurred yearly at lambing time and resolved when lambing was over. Histology: heavy dermal perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate with normal overlying epidermis. What is the diagnosis?
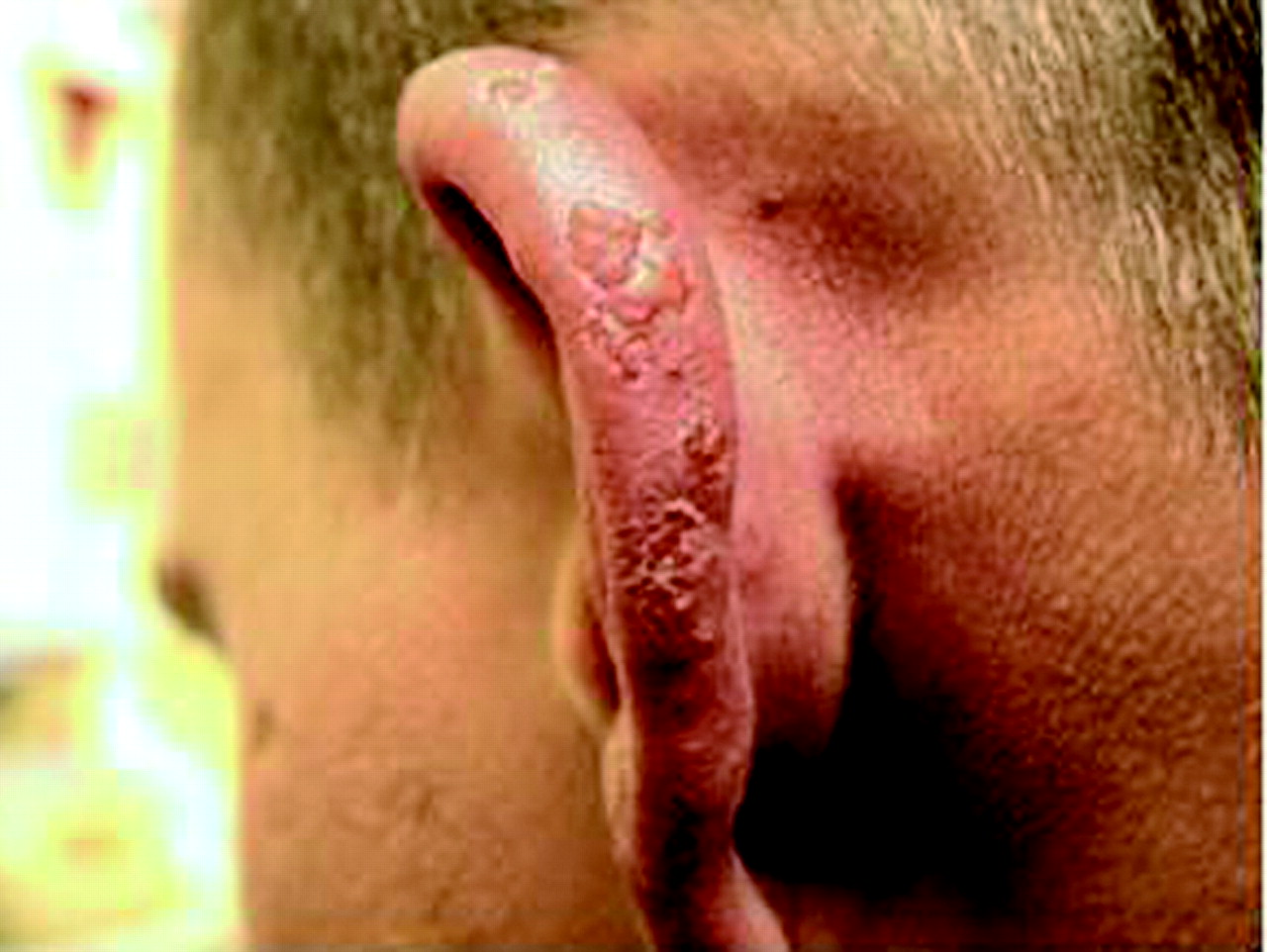
|
Juvenile spring eruption
|
|
Orf virus infection
|
|
Lupus erythematosus
|
|
Q fever
|
|
Lambing ear
|
(BMJ) - A 37-yo man presented w/ swelling of the left ear for 10 days without hx of trauma. Antibiotics, aspiration, and I&D were ineffective and cultures of the aspirated fluid were negative. What is the diagnosis?
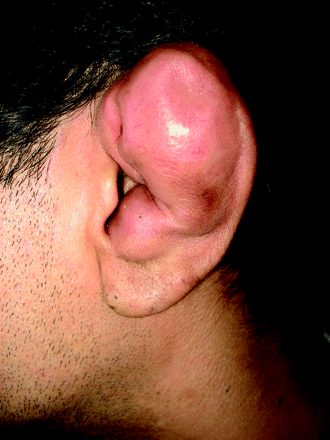
|
Relapsing polychondritis
|
|
Allergic dermatitis
|
|
Auricular tuberculosis
|
|
Chondrodermatitis nodularis helicis
|
|
Pseudocyst of the pinna
|
