(BMJ) - A 72-yo woman presented with an erythematous rash on her abdomen with induration and nodules. A biopsy confirmed the diagnosis. What is it?
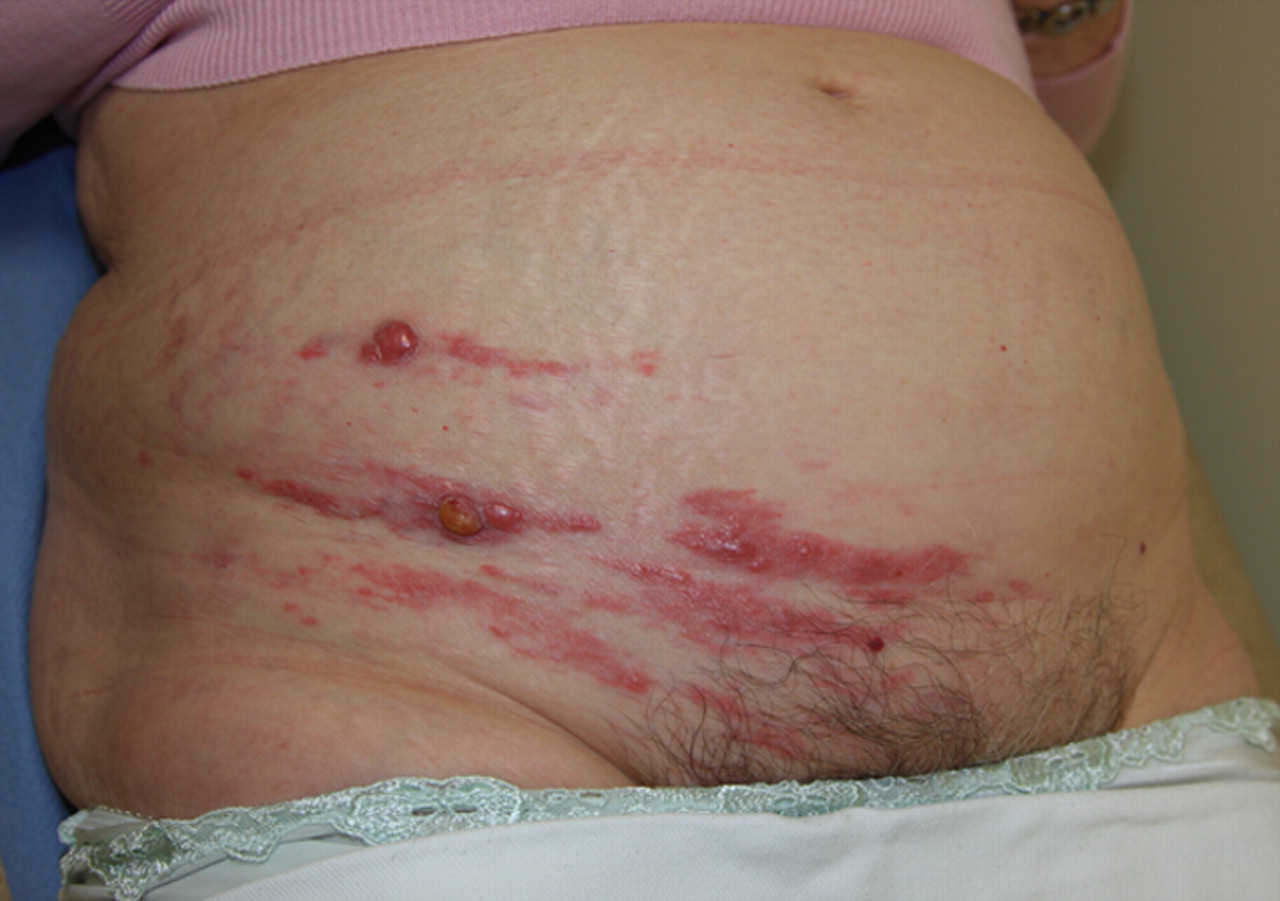
|
Contact dermatitis
|
|
Herpes zoster
|
|
Caput medusae
|
|
Lymphangitis carcinomatosa
|
|
Erysipelas
|
(BMJ) - A 36-yo man with HIV, Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia, and a CD4 count of 23 presented with an itchy rash on his hands, ears, and scalp. Other family members also had itchy rashes for months. What is the diagnosis?
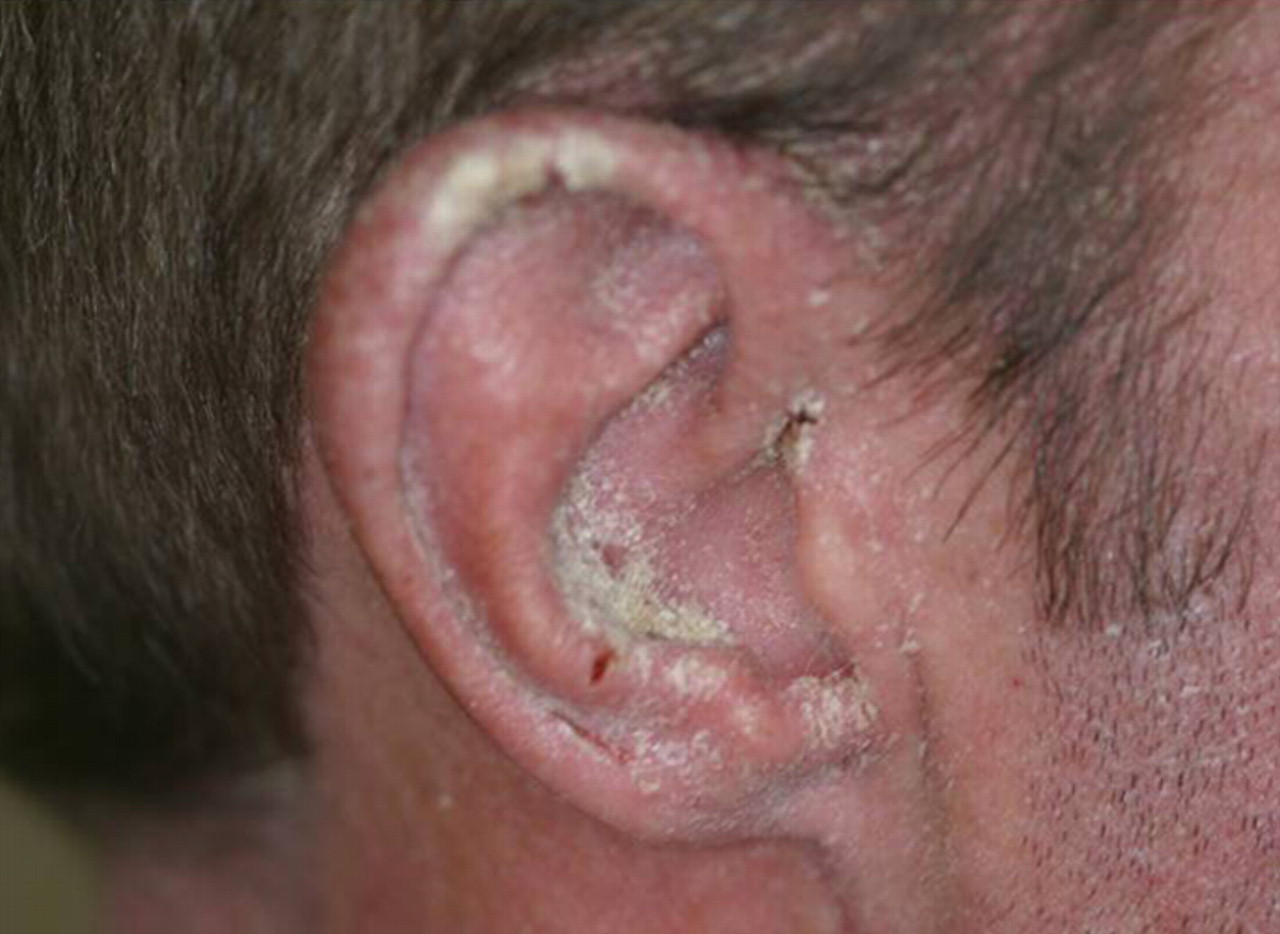
|
Crusted scabies
|
|
Darier disease
|
|
Contact dermatitis
|
|
Bed bug bites
|
|
Lichen planus
|
(BMJ) – A 25-yo man w/ short bowel syndrome received several IV abx and antifungals for Hickman line sepsis. Within 48 h, he developed a well-demarcated, exfoliative rash on his buttocks. No other inciting factors were present. What is it?
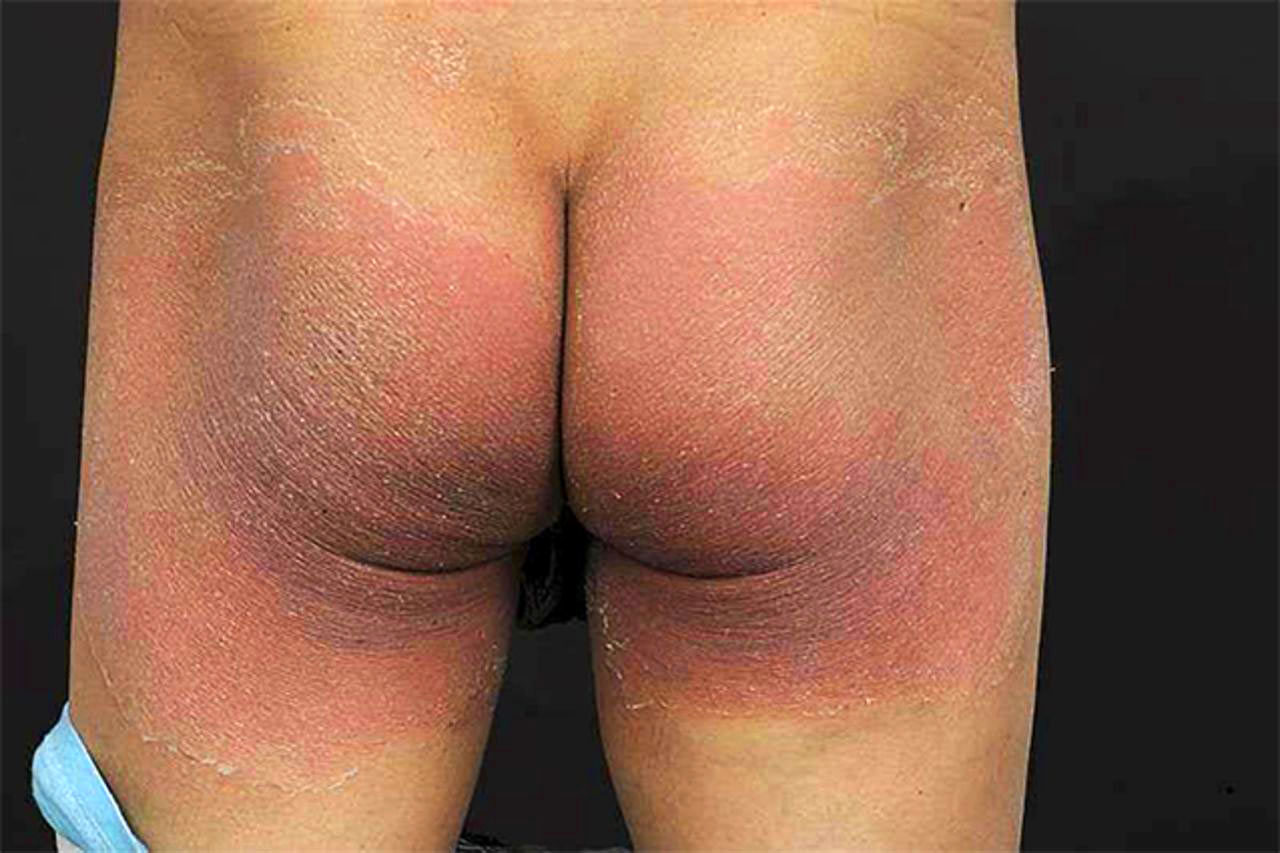
|
Erythroderma
|
|
Contact dermatitis
|
|
Baboon syndrome
|
|
Thermal burn
|
|
Tinea corporis
|
(BMJ) – An 82-yo man presented w/ acute onset throat pain and dysphagia upon wakening. His wife recalled him suddenly beginning to snore the night before. PMHx: A-fib. Meds: warfarin. Labs: INR 3.4. What is the diagnosis?
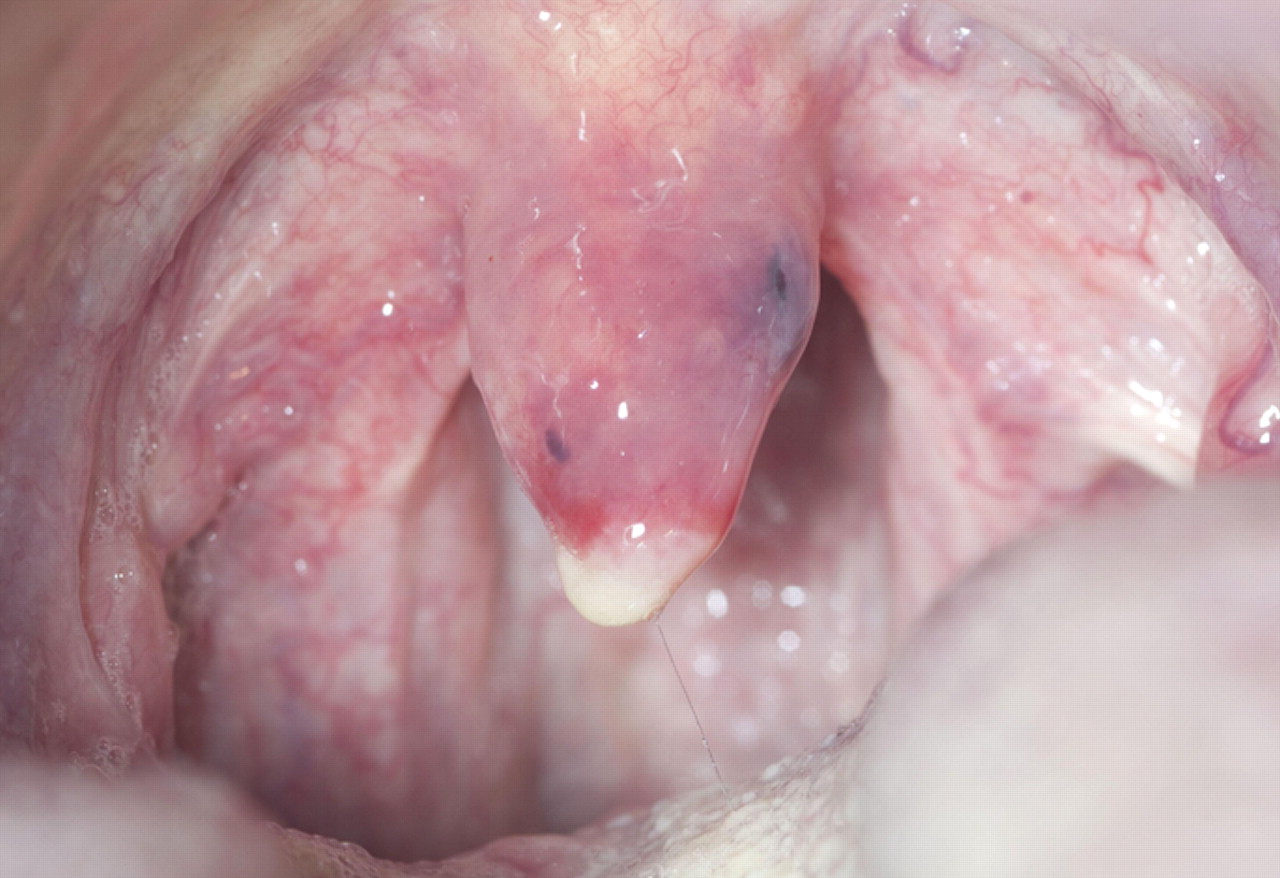
|
Aphthous ulcers
|
|
Uvular hematoma
|
|
Behcet syndrome
|
|
Oropharyngeal cancer
|
|
Strep pharyngitis
|
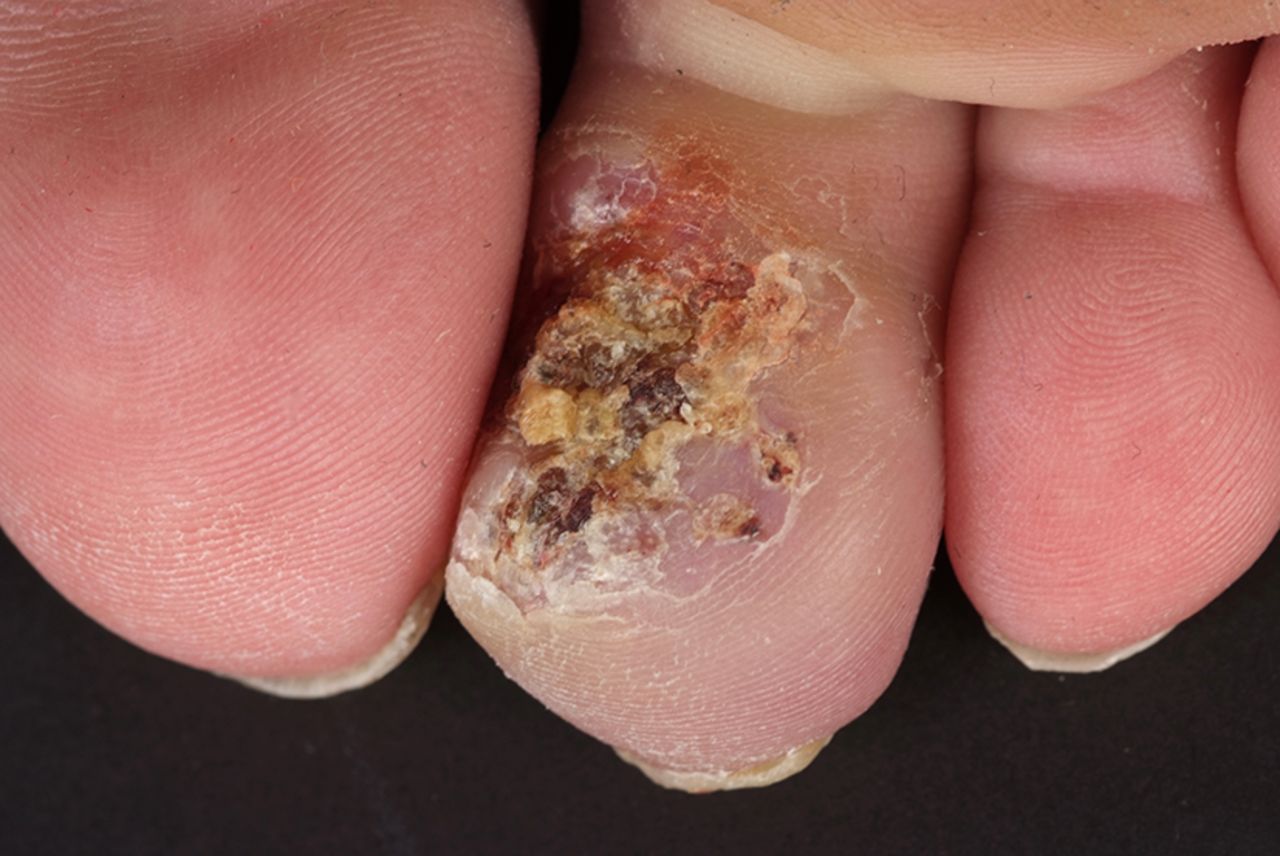
(BMJ) – A 48-yo woman presented with a presumed verruca on the underside of her second toe. The lesion had not responded to topical or oral antibiotics and was acutely tender, macerated, and hyperkeratotic. What is it?
|
Squamous cell carcinoma
|
|
Tinea pedis
|
|
Prurigo nodularis
|
|
Spider bite
|
|
Acral lentiginous melanoma
|
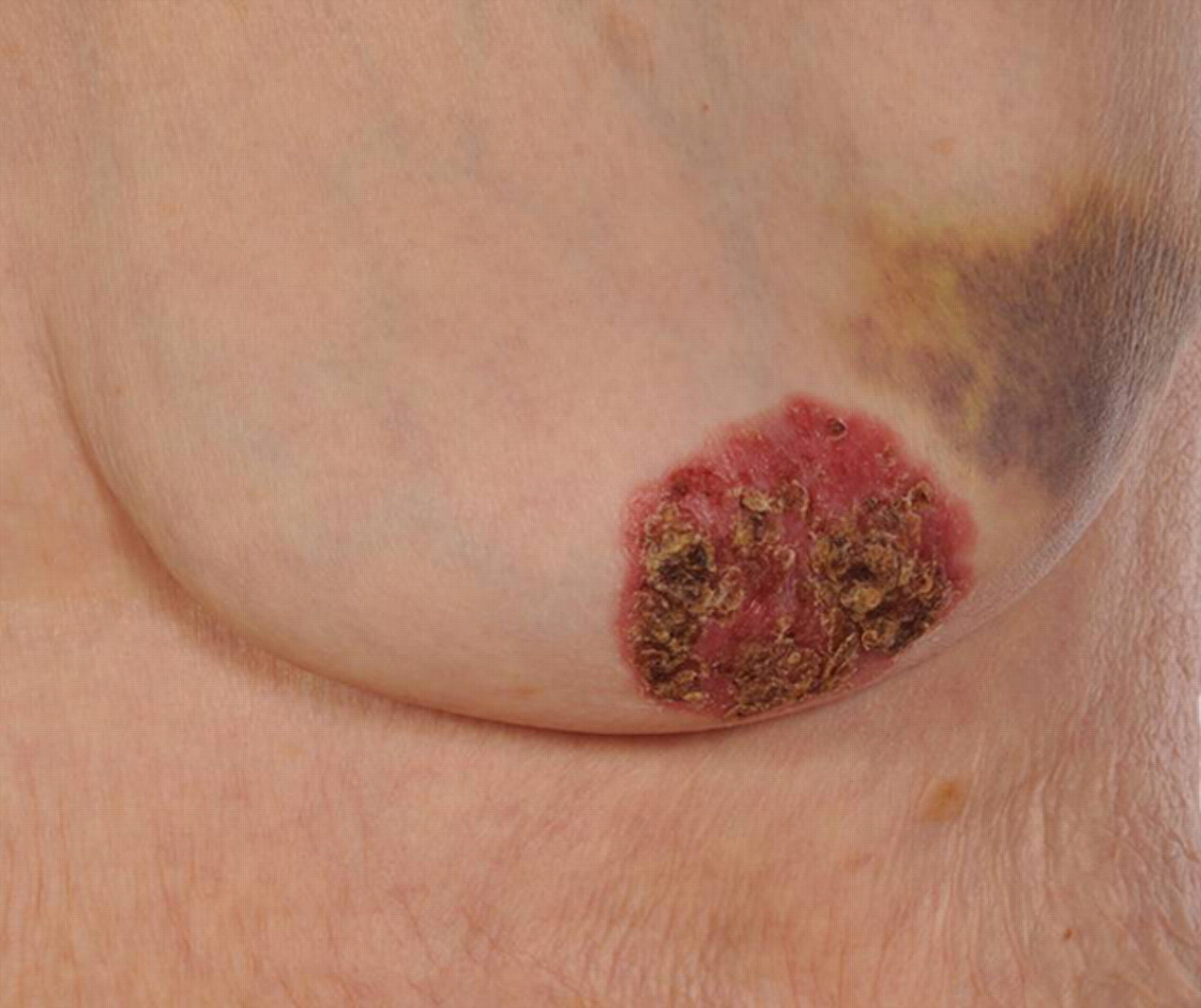
(BMJ) - A 91-yo woman w/ a family hx of breast cancer presents w/ redness of left breast and nipple x 1 yr. Exam: red, crusty nipple-areolar complex w/ nipple destruction. A 4-wk trial of steroid cream did not lead to improvement. What is the diagnosis?
|
Actinic keratosis
|
|
Eczema
|
|
Impetigo
|
|
Malignant melanoma
|
|
Paget disease
|
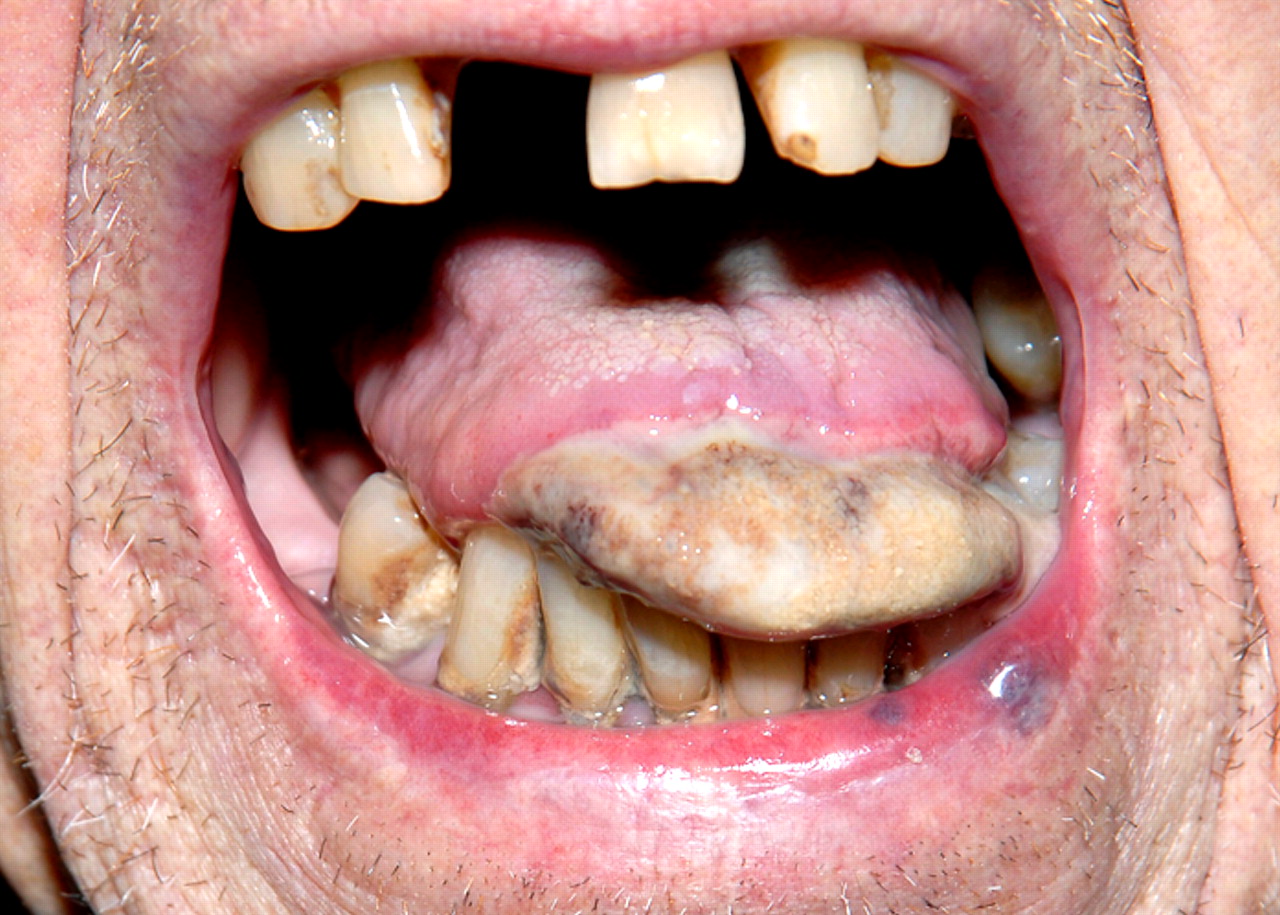
(BMJ) - An 82-yo man c/o 10 days of pain and color change in his tongue associated w/ a headache. Exam: grey-black discoloration of distal tongue and scalp tenderness. Labs: elevated inflammatory markers. What is the diagnosis?
|
Methamphetamine abuse
|
|
Giant cell arteritis
|
|
Syphilis
|
|
Necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis
|
|
Oral melanoma
|
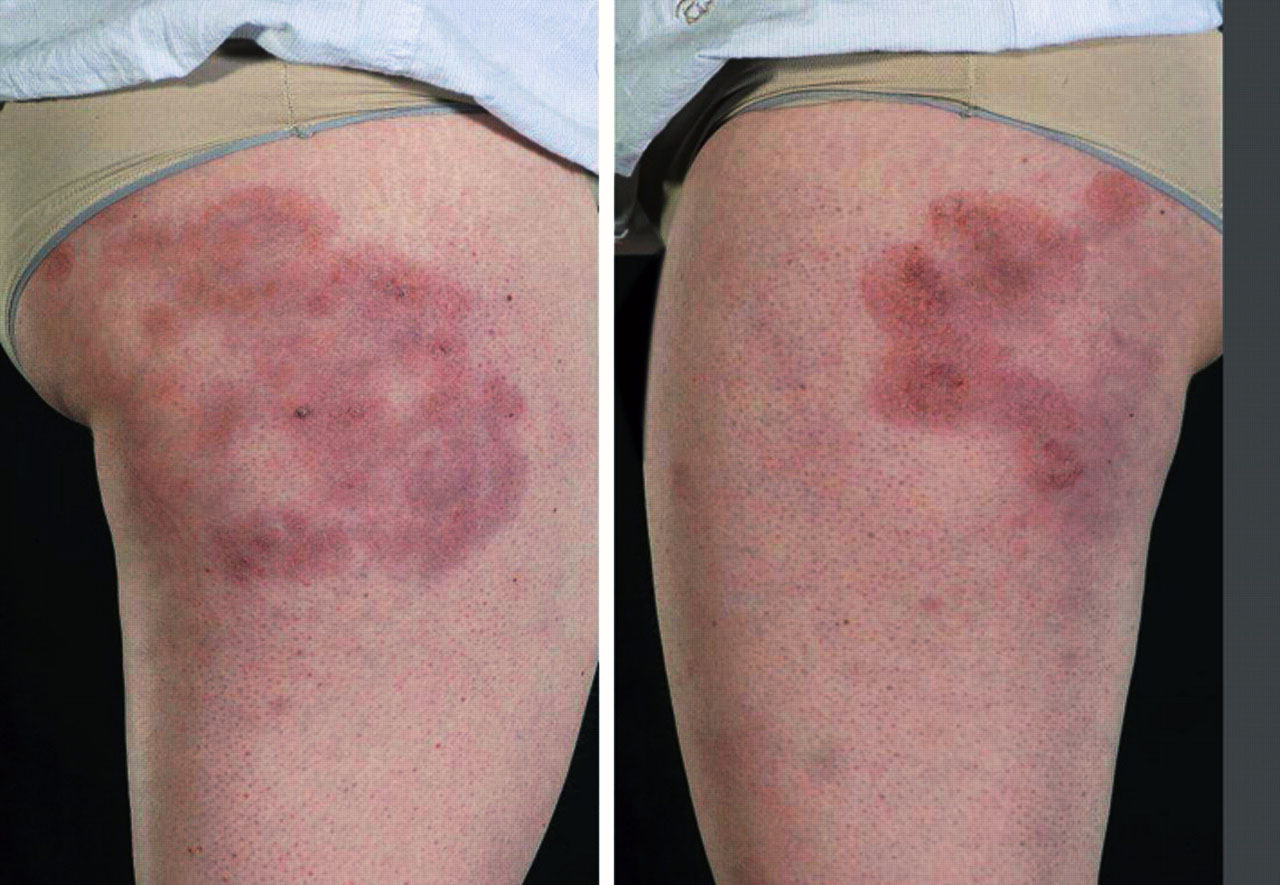
(BMJ) - A 20-yo female horse rider presented w/ painful lesions on her outer thighs during winter for 5 yrs. Exam: red, indurated, tender plaques on lateral thighs. Labs: vasculitis screen, serum cryoglobulins, and cold agglutinins all normal. What is the diagnosis?
|
Erythema chronicum migrans
|
|
Tinea corporis
|
|
Lichen planus
|
|
Frostbite
|
|
Equestrian perniosis
|
